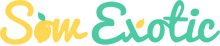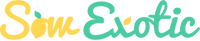Fig 'Yellow Long Neck' (Ficus carica)
Jumbo Golden Figs with a Light, Honey-Sweet Flavor
The Yellow Long Neck Fig (Ficus carica 'Yellow Long Neck') is a unique and highly sought-after fig variety known for its giant, elongated golden fruit with incredibly sweet, smooth, and mild flavor. The skin ripens to a rich yellow hue, and the light amber flesh is honeyed, juicy, and practically melts in your mouth—ideal for eating fresh or drying for later use.
This variety is known for producing very large fruit, some of the biggest among common figs, and it's self-fertile, productive, and fast-growing. It thrives in full sun, prefers well-drained soil, and performs beautifully in containers or in-ground. It's a great choice for warm, dry climates but also adaptable with care in subtropical regions.
Whether you're a fig collector or just looking to grow your own mild, honey-sweet figs, Yellow Long Neck is a rewarding and attractive addition to any edible landscape or patio orchard.
| Italian Honey | Yellow Long Neck | Violette de Bordeaux | Olympian | Royal Vineyard | Brown Turkey | Little Ruby | Celeste | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ficus carica 'Italian Honey' | Ficus carica 'Yellow Long Neck' | Ficus carica 'Violette de Bordeaux' | Ficus carica 'Olympian' | Ficus carica 'Royal Vineyard' | Ficus carica 'Brown Turkey' | Ficus carica 'Little Ruby' | Ficus carica 'Celeste' |
| Common Names | Italian Honey, Lattarulla, White Marseilles | Yellow Long Neck Fig | Violette de Bordeaux, Negronne Fig | Olympian Fig | Royal Vineyard Fig | Brown Turkey Fig | Little Ruby Fig | Celeste Fig, Sugar Fig |
| Family | Moraceae | Moraceae | Moraceae | Moraceae | Moraceae | Moraceae | Moraceae | Moraceae |
| Origin | Italy (Mediterranean) | Mediterranean cultivar | France | Washington State, USA | Mediterranean | Mediterranean | Cultivated variety | Southeastern U.S. heirloom |
| Plant Type | Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Dwarf Deciduous Fruiting Tree | Deciduous Fruiting Tree |
| Life Cycle | Perennial | Perennial | Perennial | Perennial | Perennial | Perennial | Perennial | Perennial |
| Food Forest Layer | Low Tree / Shrub Layer | Low Tree / Shrub Layer | Shrub / Low Tree Layer | Shrub / Low Tree Layer | Shrub / Low Tree Layer | Low Tree / Shrub Layer | Shrub / Low Tree Layer | Shrub / Low Tree Layer |
| Mature Size | 10–15 ft (smaller with pruning) | 8–15 ft | 6–10 ft (smaller with pruning) | 8–12 ft (prunable) | 8–12 ft | 10–20 ft (prunable) | 3–6 ft (dwarf) | 8–15 ft (prunable) |
| Light | Full Sun | Full Sun | Full Sun | Full Sun | Full Sun | Full Sun | Full Sun | Full Sun |
| Water Needs | Moderate; drought-tolerant | Moderate; well-draining soil | Moderate; well-draining soil | Moderate; well-draining soil | Moderate; well-draining soil | Moderate; drought-tolerant | Moderate; well-draining soil | Moderate; well-draining soil |
| Harvest Season | Early + Late Summer | Mid to Late Summer | Early + Late Summer | Mid to Late Summer | Mid to Late Summer | Early + Late Summer | Summer to Fall | Summer (main); early breba possible |
| Time to Fruit | 1–2 years | 1–2 years | 1–2 years | 1–2 years | 1–2 years | 1–2 years | 1–2 years | 1–2 years |
| Self-Fertile | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Growth Rate | Fast | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Fast | Fast | Fast |
| Zones | 7–10 | 7–10 | 7–10 | 6–10 | 7–10 | 7–10 | 7–10 | 7–10 |
| Florida Native | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Propagation | Cuttings | Cuttings | Cuttings | Cuttings | Cuttings | Cuttings | Cuttings | Cuttings |
| Seasonal Characteristics | Deciduous; fruits on new wood | Deciduous; fruits on new wood | Deciduous; fruits on new wood | Deciduous; cold-hardy to 0°F | Deciduous; fruits on new wood | Deciduous; fruits on new wood | Deciduous; fruits on new wood | Deciduous; winter dormant |
Our Yellow Long Neck Fig plants are shipped in 4" biodegradable coconut coir planters that can be planted directly in the soil, promoting strong root growth and ensuring an eco-friendly start.
Climate and Soil Requirements
- Climate: Best suited for warm, Mediterranean-like climates. Ideal USDA hardiness zones are 7-10. It can tolerate some frost but prefers a sheltered location if grown in colder areas.
- Soil: Prefers well-draining soil, rich in organic matter. Slightly acidic to neutral pH levels are ideal. Avoid heavy clay soils unless amended to improve drainage.
Planting
- Location: Choose a sunny location that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. In colder regions, consider planting near a south-facing wall for added warmth.
- Soil Preparation: Ensure the soil is well-draining and amend with compost or organic matter to improve fertility and drainage.
- Spacing: Space trees 10-15 feet apart to allow for adequate growth and air circulation. For container planting, choose a large pot with good drainage.
Watering
- Establishment Phase: Water regularly to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged during the first year.
- Mature Plants: Once established, fig trees are somewhat drought-tolerant. Water deeply and less frequently, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings.
Sunlight
- Outdoor Plants: Require full sun for optimal growth and fruit production. Ensure they receive at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Indoor/Container Plants: Place in the sunniest spot available, preferably near a south-facing window.
Fertilizing
- Growing Season: Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring as new growth begins. Supplement with a high-potassium fertilizer during the fruiting period to enhance fruit development.
- Frequency: Fertilize every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. Reduce feeding in the fall and avoid fertilizing in winter.
Pruning
- Routine Pruning: Prune in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Remove dead, diseased, or weak branches to maintain the tree's shape and improve air circulation.
- Fruit Production: Light pruning helps encourage new growth and increased fruit production. Avoid heavy pruning, which can reduce yields.
Pest and Disease Management
- Common Pests: Monitor for aphids, scale, and spider mites. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil as needed to control infestations.
- Diseases: Watch for fungal diseases such as leaf spot or rust. Ensure proper spacing and good air circulation to minimize issues. Use fungicides if necessary.
Harvesting Fruit
- When to Harvest: Fruits are ready to harvest when they are fully colored and slightly soft to the touch. They should easily detach from the tree.
- Usage: Enjoy fresh, dried, or use in cooking and baking. Yellow Long Neck Figs are particularly sweet and delicious, making them perfect for preserves and desserts.
Winter Care
- Outdoor Plants: In regions prone to frost, protect trees with frost cloth or burlap during cold snaps. Mulch around the base to insulate the roots.
- Indoor/Container Plants: Move containers to a sheltered location or indoors during the winter. Maintain a consistent temperature and humidity level.


Wondering about your USDA Growing Zone and what you can grow? 🌎🌿 Learn how to find your Zone and grow tropical plants anywhere—Florida to Alaska! 👉 Read the full blog here!
We ship every plant plastic-free and planet-friendly—using compostable packaging, recyclable pots, and carbon-conscious shipping from start to finish. 🌎🌱👉 Our Commitment to Packaging & Shipping Sustainability